ROOT CANAL TREATMENT


عصب کشی
خیلی از شماها حد اقل یک بار عصب کشی را تجربه کرده اید .... معمولا کسی که کارش به عصب کشی میرسد قبل از اون یک دوره درد دندان را تحمل کرده است و معمولا خود مراحل عصب کشی هم ممکن است همراه با درد باشد و در نهایت بعد از عصب کشی هم ممکن است چند روزی درد داشته باشیم ..... همه اینها باعث میشود که عصب کشی یاد آور درد برایمان باشد بریم سر اصل مطلب ....

۱- با ساختمان دندان سالم آشنا شدید اینهم تصویر دندانی که دچار پوسیدگی شده و به عصب رسیده .... ورود میکروبها به پالپ دندان باعث ایجاد التهاب در پالپ شده و این التهاب باعث افرایش حجم پالپ شده و با توجه به اینکه پالپ دندان در یک محفظه بسته واقع شده باعث افزایش شدید فشار داخلی پالپ میشود .... این افزایش فشار منجر به فشار آمدن به پایانه های عصب دندان شده و دندان درد شروع میشود .... علت اینکه دندان درد شبها بیشتر است این است که موقعی که دراز میکشیم این فشار داخلی پالپ دندان باز هم بیشتر میشود.... در زمانهای قدیم به تجربه دریافته بودند و سیخ داغ شده به محل پوسیدگی وارد میکردند دندان درد خوب میشد ... علت آن بود که با سوراخ کردن سقف پالپ و جاری شدن خون فشار داخل پالپ کاهش پیدا کرده و درد کم میشد .... ماهم در مطب جلسه اول چنین کاری میکنیم البته مدرنتر ؟!.... و با بیحسی و فرز و توربین دندانپزشکی پالپ را باز کرده و پانسمان میکنیم و این کار باعث خوب شدن دندان درد میشود

۲- بعد از تمیز کردن و برداشتن پوسیدگی به کانالهای داخل ریشه دسترسی پیدا میکنیم .... این کانالها باید از هر نوع بافت نرم و احتمالا میکروبها و .... پاکسازی شده و کانالها فرم داده شوند .... این کار به وسیله فایلها انجام میشود و بعد از این مرحله کانالهای ریشه آماده پر کردن میشود .

۳- کانالهای ریشه با موادی به نام گوتا پرکا پر میگردد... این مواد سازگار با نسوج انسانی است و موادی همراه دارد که باعث مشاهده آن توسط رادیوگرافی میشود و در ضمن توانائی شکل پذیری و فشرده شدن را پیدا میکنن ... تا این مرحله به دو بار رادیو گرافی نیاز است تا بشود طول کامل ریشه دندان را اندازه گرفته و از پر شدن کامل ریشه مطمئن شد .... پر کردن کامل و سیل آن اهمیت بسزائی دارد و عدم مهر و موم شدم کامل ریشه باعث شکست درمان ریشه دندان خواهد شد ...بعد از پر کردن ریشه معمولا دندان با پانسمان موقت پر میشود به دو علت .... اول اینکه این درمانها وقت گیر است و معمولا بیمار خسته میشود .... در ثانی این کارها احتمال درد و ناراحتی های بعد عصب کسی را به همراه دارد که معمولا پر کردن کامل را برای جلسه بعد و اطمینان از قطع شدن درد احتمالی موکول میکنیم ....

۴-ترمیم تاج دندانهای عصب کشی شده باید با دقت صورت بگیرد چون هم نسج دندانی زیادی تخریب شده و هم به علت عصب کشی دندان خشک و شکننده میشود .... معمولا دندانهای عصب کشی شده باید با پین داخل کانال همراه با یک ماده محکم مثل آمالگام پر شده و بعد حتما روکش گردد ... هر چند روکش دندان هزینه بردار است اما ارزش آن را دارد که از شکست احتمالی دیواره های دندان جلو گیری کند.... ...معمولا ضایعات نوک ریشه و آبسه احتمالی با یک درمان خوب ریشه بهبودی پیدا میکند
اندو یا اندودونتیکس(درمان ریشه دندان) چیست ؟
درمان بیماریها وصدمات پالپ و بافتهای اطراف ریشه مرتبط با پالپ می باشد. درمان پالپ دندان با نامهای روت کانال، اندو، عصب کشی و… شناخته می شود
بیان اینکه دندانی احتیاج به معالجه ریشه دارد و یا به اصطلاح عامیانه عصب کُشی یا عصب کِشی شود در بسیاری از بیماران ایجاد هراس و اضطراب می کند و اغلب ترس آنها ناشی از مطالب نادرستی است که در این زمینه شنیده اند. بسیاری از بیمارانی که جهت خلاصی از درد فوراً اقدام به کشیدن آن نموده اند، بعداً پشیمان شده و آرزو می کنند که ای کاش با معالجه ریشه، دندان را نجات داده بودند. خصوصاً آنهایی که جهت جایگزینی آن دندانها با پروتزهای ثابت از هزینه گران این خدمات آگاهی می یابند.
تعریف اندو یا اندودونتیکس؟
دندان مرکب از یک ساختمان سختی است که بافت نرم زنده ای را احاطه کرده است. این قسمت نرم مرکزی، پالپ (دراصطلاح عامیانه، عصب) نام دارد که شامل سلولها، عروق خونی واعصاب می باشد. اندودونتیکس شاخه ای از علم دندانپزشکی است که وظیفه تشخیص و درمان پالپهای آماسی و بیمار شده را به عهده دارد.
چه عواملی سبب آماس و بیماری پالپ می گردند؟
پوسیدگیهای دندانی اگر درمان نشوند، بعد از تخریب مینا و عاج به پالپ رسیده و باعث التهاب و ناراحتی آن می گردند. علاوه بر پوسیدگی، عوامل دیگری چون سابقه ضربه ناگهانی به دندان، پرکردگی های عمیق، شکستگی و ترک دندان، تحلیل و سایش شدید دندانها و بیماریهای پیشرفته لثه در ایجاد آماس و بیماری پالپ نقش دارند.
علائم بیماری پالپ چیست؟
برخی از علائم پالپ آماسی شامل درد ادامه داربه هنگام نوشیدن مایعات سرد و یا گرم، درد خود بخودی، درد هنگام جویدن و یا حتی موقع دراز کشیدن می باشد. گاهی نیز با توجه به سیر بیماری پالپ، ممکن است بیمار درد نداشته باشد. علائم ظاهری پالپ بیمار ممکن است وجود پوسیدگی عمیق و یا وجود ضایعه در انتهای ریشه، تورم و یا تخلیه چرک از دندان و یا انتهای آن باشد.
فوائد معالجه عصب چیست؟
۱ – دندان حفظ می شود. ۲- وجود دندان باعث حفظ استخوان نگهدارنده آن می گردد.
۱ – دندان حفظ می شود. ۲- وجود دندان باعث حفظ استخوان نگهدارنده آن می گردد.
عوارض عدم درمان چیست؟
۱ – آبسه ۲- درد ۳- عفونت شدید ۴- نهایتاً از دست دادن دندان خواهد بود.
۱ – آبسه ۲- درد ۳- عفونت شدید ۴- نهایتاً از دست دادن دندان خواهد بود.
درمان جایگزین چیست؟
در بعضی موارد و شرایط می توان معالجه ریشه را به اندکی بعد موکول کرد. در مواردی که دندان کشیده می شود درمان ، جایگزینی آنها با دندانهای مصنوعی (پروتز ثابت و یا ایمپلنت) می باشد که به مراتب گرانتر است.
در بعضی موارد و شرایط می توان معالجه ریشه را به اندکی بعد موکول کرد. در مواردی که دندان کشیده می شود درمان ، جایگزینی آنها با دندانهای مصنوعی (پروتز ثابت و یا ایمپلنت) می باشد که به مراتب گرانتر است.
چند جلسه وقت برای درمان ریشه دندان لازم است؟
معالجه ریشه اکثر دندانها را می توان در یک جلسه انجام داد ولی بعضی از دندانها ممکن است به دو یا چند جلسه زمانی نیاز داشته باشند که در این موارد دندانها در پایان جلسات معمولاً پانسمان موقت می گردند.
معالجه ریشه اکثر دندانها را می توان در یک جلسه انجام داد ولی بعضی از دندانها ممکن است به دو یا چند جلسه زمانی نیاز داشته باشند که در این موارد دندانها در پایان جلسات معمولاً پانسمان موقت می گردند.
موفقیت درمان چقدر است؟
در صورتی که درمان ریشه بطور کامل و استاندارد انجام شود از موفقیت بالائی برخوردار است.
در صورتی که درمان ریشه بطور کامل و استاندارد انجام شود از موفقیت بالائی برخوردار است.
چه عواملی باعث عدم موفقیت در درمان ریشه می گردد؟
علاوه بر اشکالات تکنیکی و اتفاقات حین کار، انحنای زیاد ریشه ها، وجود کانالهای جانبی، دفاع بدن و … ممکن است معالجه ریشه دندان را بخطر اندازد.
علاوه بر اشکالات تکنیکی و اتفاقات حین کار، انحنای زیاد ریشه ها، وجود کانالهای جانبی، دفاع بدن و … ممکن است معالجه ریشه دندان را بخطر اندازد.
آیا اگر عصب درآورده شود، دندان می میرد؟
خیر، دندان بعد از معالجه ریشه(عصب) هنوز زنده می ماند چونکه تغذیه خارجی آن از سمت بافتهای در برگیرنده هنوز ادامه دارد. البته این زنده ماندن به معنای آن نیست که دندان مثل دیگر دندانها به تحریکات حرارتی و الکتریکی پاسخ مثبت دهد.
خیر، دندان بعد از معالجه ریشه(عصب) هنوز زنده می ماند چونکه تغذیه خارجی آن از سمت بافتهای در برگیرنده هنوز ادامه دارد. البته این زنده ماندن به معنای آن نیست که دندان مثل دیگر دندانها به تحریکات حرارتی و الکتریکی پاسخ مثبت دهد.
آیا پس از معالجه ریشه درد وجود دارد؟
معمولاً مقداری درد و ناراحتی گذرای خفیف تا متوسط به دنبال از بین رفتن بیحسی تا چند روز وجود داشته که با تجویز مسکن های ضد التهاب تسکین می یابد. غالباً، ناراحتی و درد آنچنان نیست که مانع فعالیت های روزانه شود. در مواردی که درد زیاد است میتوانید با دندانپزشک معالج تماس بگیرید.
معمولاً مقداری درد و ناراحتی گذرای خفیف تا متوسط به دنبال از بین رفتن بیحسی تا چند روز وجود داشته که با تجویز مسکن های ضد التهاب تسکین می یابد. غالباً، ناراحتی و درد آنچنان نیست که مانع فعالیت های روزانه شود. در مواردی که درد زیاد است میتوانید با دندانپزشک معالج تماس بگیرید.
آیا دندان بعد از معالجه ریشه تیره می شود؟
سابقاً دندانهایی که درمان ریشه می شدند به مرور تیره تر می گشتند، ولی امروزه با پیشرفت های تکنیکی احتمال این تغییر رنگ ناچیز بوده و اگر اتفاق افتاد، نیز با استفاده از روشهای سفید کردن و یا روکش های چینی و لامینت می توان با آن مقابله کرد.
سابقاً دندانهایی که درمان ریشه می شدند به مرور تیره تر می گشتند، ولی امروزه با پیشرفت های تکنیکی احتمال این تغییر رنگ ناچیز بوده و اگر اتفاق افتاد، نیز با استفاده از روشهای سفید کردن و یا روکش های چینی و لامینت می توان با آن مقابله کرد.
بعد از درمان ریشه، تاج دندان چگونه و با چه موادی باید ترمیم شود؟
نحوه ترمیم تاج دندان بستگی به نسج باقیمانده و دندان مبتلا دارد. در دندانهایی که متحمل نیروهای سنگین جویدن هستند و یا پوسیدگی آنها شدید بوده توصیه می گردد که با ترمیم های مطمئن تری چون روکش های فلزی و چینی بازسازی شوند.
نحوه ترمیم تاج دندان بستگی به نسج باقیمانده و دندان مبتلا دارد. در دندانهایی که متحمل نیروهای سنگین جویدن هستند و یا پوسیدگی آنها شدید بوده توصیه می گردد که با ترمیم های مطمئن تری چون روکش های فلزی و چینی بازسازی شوند.
جراحی اندودونتیک یعنی چه؟
در مواردی که درمان معالجه ریشه دندان به شکست می انجامد. هنوز می توان دندان را نجات داد. در این موارد بعد از انجام بیحسی، دندانپزشک بافت لثه را به آرامی کنار زده و بافتهای آماسی انتهای ریشه را خارج نموده و یک پرکردگی نیز در ته ریشه جهت ممانعت از عود ضایعه قرار می دهد.
در مواردی که درمان معالجه ریشه دندان به شکست می انجامد. هنوز می توان دندان را نجات داد. در این موارد بعد از انجام بیحسی، دندانپزشک بافت لثه را به آرامی کنار زده و بافتهای آماسی انتهای ریشه را خارج نموده و یک پرکردگی نیز در ته ریشه جهت ممانعت از عود ضایعه قرار می دهد.
بعد از انجام درمان ریشه و ترمیم نهایی آن، آیا اقدام دیگری لازم است؟
ضروری است جهت ارزیابی موفقیت درمان در طولانی مدت، ظرف ۶ ماه تا یکسال آینده مجدداً ویزیت بعمل آید. در این ویزیت دندانپزشک موفقیت درمان، سلامت انساج لثه و ترمیم نهایی را ارزیابی می کند.
ضروری است جهت ارزیابی موفقیت درمان در طولانی مدت، ظرف ۶ ماه تا یکسال آینده مجدداً ویزیت بعمل آید. در این ویزیت دندانپزشک موفقیت درمان، سلامت انساج لثه و ترمیم نهایی را ارزیابی می کند.
مراحل درمان چگونه است؟
بعد از انجام بیحسی(در مواردیکه نیاز باشد)، درمان شامل مراحل زیر است:
مرحله یک: دستیابی به کانال
مرحله دوم: تعیین طول ریشه
مرحله سوم: تمیز کردن و شکل دادن کانال ها
مرحله چهارم: پرکردن کانال
مرحله پنجم: ترمیم موقت
مرحله ششم: ترمیم دائم
بعد از انجام بیحسی(در مواردیکه نیاز باشد)، درمان شامل مراحل زیر است:
مرحله یک: دستیابی به کانال
مرحله دوم: تعیین طول ریشه
مرحله سوم: تمیز کردن و شکل دادن کانال ها
مرحله چهارم: پرکردن کانال
مرحله پنجم: ترمیم موقت
مرحله ششم: ترمیم دائم
معالجه ریشه دندان (Root canal Therapy )
لابد همه این ضرب المثل که می گوید:دندانی را که درد می کند باید کشید را شنیده اید. ما هم بسیار شنیده ایم، ولی باید توجه داشت که سابقه این ضرب المثل مربوط به زمانی است که علم دندانپزشکی وجود نداشته و افرادی بی صلاحیت مثل سلمانی ها عهده دار امور دندانپزشکی بودند. دندانپزشکان امروزی نه تنها درد را از بین برده،بلکه باعث تگهداری دندانها در دهان می شوند. از گذشته ای نه چندان دور تا بحال، عامه مردم لفظ عصب کُشی یا عصب کِشی را بجای معالجه ریشه دندان بکار می برند که چندان صحیح نبوده و آنچه که باعث رواج و شایع شدن این اصطلاحات شده، تصور مردم با توجه به از بین رفتن درد دندان بدنبال معالجه ریشه می باشد. قسمت سخت دندان تشکیل شده از میناـ عاج و سمان، که بافت نرمی را در داخل و وسط دندان بنام پالپ، احاطه کرده اند.
لابد همه این ضرب المثل که می گوید:دندانی را که درد می کند باید کشید را شنیده اید. ما هم بسیار شنیده ایم، ولی باید توجه داشت که سابقه این ضرب المثل مربوط به زمانی است که علم دندانپزشکی وجود نداشته و افرادی بی صلاحیت مثل سلمانی ها عهده دار امور دندانپزشکی بودند. دندانپزشکان امروزی نه تنها درد را از بین برده،بلکه باعث تگهداری دندانها در دهان می شوند. از گذشته ای نه چندان دور تا بحال، عامه مردم لفظ عصب کُشی یا عصب کِشی را بجای معالجه ریشه دندان بکار می برند که چندان صحیح نبوده و آنچه که باعث رواج و شایع شدن این اصطلاحات شده، تصور مردم با توجه به از بین رفتن درد دندان بدنبال معالجه ریشه می باشد. قسمت سخت دندان تشکیل شده از میناـ عاج و سمان، که بافت نرمی را در داخل و وسط دندان بنام پالپ، احاطه کرده اند.
تعریف Root canal Therapy:
این عنوان از سه کلمه Root به معنای ریشه، و Canal به معنای مجرا و Therapy به معنی معالجه تشکیل شده که مفهوم کلی آن معالجه مجرای ریشه دندان می باشد و شاخه ای از دندانپزشکی است که شامل دانش و اعمالی است که به معالجه و حفظ ریشه دندان می پردازد.
این عنوان از سه کلمه Root به معنای ریشه، و Canal به معنای مجرا و Therapy به معنی معالجه تشکیل شده که مفهوم کلی آن معالجه مجرای ریشه دندان می باشد و شاخه ای از دندانپزشکی است که شامل دانش و اعمالی است که به معالجه و حفظ ریشه دندان می پردازد.
پالپ چیست؟
پالپ دندان بافت نرمی است که در داخل دندان قرار گرفته و شامل عروق و اعصاب و سلولهایی می باشد. حس، تغذیه، عاج سازی و دفاع میکروبی از اعمال پالپ بشمار می آیند.
پالپ دندان بافت نرمی است که در داخل دندان قرار گرفته و شامل عروق و اعصاب و سلولهایی می باشد. حس، تغذیه، عاج سازی و دفاع میکروبی از اعمال پالپ بشمار می آیند.
چه عواملی باعث آسیب و صدمه با پالپ دندان می شوند؟
عوامل متعددی سبب آسیب به پالپ می گردند که عمده ترین آن تأخیر در ترمیم پوسیدگی ها و نتیجتاً گسترش آنها به پالپ دندان است که سبب آلودگی پالپ به میکروبهای دهان می شود. پالپ دندان همچنین ممکن است بر اثر ضربه ای ناگهانی حتی در مواردی چون ضربه قاشق و یا شکستن تخمه، پسته و بادام دچار التهاب و مرگ شود. ترکهای دندان، پرکردگی های وسیع و بعضی از مواد ترمیمی نیز سبب ساز هستند.
عوامل متعددی سبب آسیب به پالپ می گردند که عمده ترین آن تأخیر در ترمیم پوسیدگی ها و نتیجتاً گسترش آنها به پالپ دندان است که سبب آلودگی پالپ به میکروبهای دهان می شود. پالپ دندان همچنین ممکن است بر اثر ضربه ای ناگهانی حتی در مواردی چون ضربه قاشق و یا شکستن تخمه، پسته و بادام دچار التهاب و مرگ شود. ترکهای دندان، پرکردگی های وسیع و بعضی از مواد ترمیمی نیز سبب ساز هستند.
نحوه معالجه ریشه دندان چگونه است؟
دندانپزشک بعد از بی حس نمودن دندان ( در مواردیکه لازم است) اقدام به برداشتن پوسیدگی و تراش حفره دسترسی به پالپ دندان نموده و پالپ عفونی و بیمار را از ریشه خارج می کند و بعد از تمیز نمودن و خشک کردن مجرای ریشه و دندان جای خالی پالپ را با موادی که به همین منظور ساخته شده اند پر می کند و سپس ترمیم قسمت تاجی دندان صورت میگیرد.
دندانپزشک بعد از بی حس نمودن دندان ( در مواردیکه لازم است) اقدام به برداشتن پوسیدگی و تراش حفره دسترسی به پالپ دندان نموده و پالپ عفونی و بیمار را از ریشه خارج می کند و بعد از تمیز نمودن و خشک کردن مجرای ریشه و دندان جای خالی پالپ را با موادی که به همین منظور ساخته شده اند پر می کند و سپس ترمیم قسمت تاجی دندان صورت میگیرد.
آیا همه دندانها به یک تعداد ریشه دارند؟
خیر، تعداد ریشه دندانها بطور معمول و طبیعی ین یک تا سه عدد می باشد ولی دندانهایی نیز وجود دارند که دارای یک یا چند ریشه اضافی هستند و در حین کار و با گرفتن رادیوگرافی کشف می گردند. بطور طبیعی دندانهای قدامی دارای یک ریشه، دندانهای آسیای کوچک دارای یک یا دو ریشه و دندانهای آسیای بزرگ سه و چهار ریشه ای هستند.
خیر، تعداد ریشه دندانها بطور معمول و طبیعی ین یک تا سه عدد می باشد ولی دندانهایی نیز وجود دارند که دارای یک یا چند ریشه اضافی هستند و در حین کار و با گرفتن رادیوگرافی کشف می گردند. بطور طبیعی دندانهای قدامی دارای یک ریشه، دندانهای آسیای کوچک دارای یک یا دو ریشه و دندانهای آسیای بزرگ سه و چهار ریشه ای هستند.
اگر پالپی که آلوده شده و ملتهب و دردناک است خارج نشود و به عبارتی معالجه انجام نگردد، چه اتفاقی می افتد؟
معمولاً درد آن بیشتر شده و بیمار را اذیت می کند، ولی مواردی وجود دارد که درد فروکش می کند. باید توجه داشت که از بین رفتن درد دندان نشانة بهبودی پالپ دندان نیست و عفونت به سیر خود ادامه می دهد. سرایت عفونت به استخوان انتهای ریشه باعث ایجاد گرانوم، کیست و یا آبسه می گردد که خود درد و ناراحتی ثانویه ای را به دنبال دارد. در صورت عدم معالجه ریشه دندان سیر بیماری نهایتاً منجر به کشیدن و یا از دست دادن دندان خواهد شد.
معمولاً درد آن بیشتر شده و بیمار را اذیت می کند، ولی مواردی وجود دارد که درد فروکش می کند. باید توجه داشت که از بین رفتن درد دندان نشانة بهبودی پالپ دندان نیست و عفونت به سیر خود ادامه می دهد. سرایت عفونت به استخوان انتهای ریشه باعث ایجاد گرانوم، کیست و یا آبسه می گردد که خود درد و ناراحتی ثانویه ای را به دنبال دارد. در صورت عدم معالجه ریشه دندان سیر بیماری نهایتاً منجر به کشیدن و یا از دست دادن دندان خواهد شد.
چه مراقبت هایی لازم است تا دندان نیاز به معالجه عصب نداشته باشد؟
با مراجعه و معاینات منظم دندانپزشکی و رعایت اصول بهداشت دهان ودندان و ترمیم پوسیدگی ها در مراحل اولیه موردی برای معالجه ریشه دندان بوجود نمی آید.
با مراجعه و معاینات منظم دندانپزشکی و رعایت اصول بهداشت دهان ودندان و ترمیم پوسیدگی ها در مراحل اولیه موردی برای معالجه ریشه دندان بوجود نمی آید.
آیا صحیح است دندانی که معالجه ریشه شده، شکننده می گردد؟
دندانی که پالپ آن درگیر می شود، معمولاً دارای پوسیدگی وسیع بوده که مقدار زیادی از مینا و عاج را از بین برده است و گاهی دندانپزشک ناچار می گردد که مقداری از نسج سالم دندان را نیز برای دسترسی به پالپ بتراشد که مجموعه این عوامل بعلاوه خشک شدن دندان بر اثر از دست دادن تغذیه داخلی سبب میگرددکه دندان ضعیف و شکننده گردد که جای نگرانی ندارد، چونکه با ترمیم های خاص و یا روکش نمودن دندان می توان بر این نقیصه، چیره شد.
دندانی که پالپ آن درگیر می شود، معمولاً دارای پوسیدگی وسیع بوده که مقدار زیادی از مینا و عاج را از بین برده است و گاهی دندانپزشک ناچار می گردد که مقداری از نسج سالم دندان را نیز برای دسترسی به پالپ بتراشد که مجموعه این عوامل بعلاوه خشک شدن دندان بر اثر از دست دادن تغذیه داخلی سبب میگرددکه دندان ضعیف و شکننده گردد که جای نگرانی ندارد، چونکه با ترمیم های خاص و یا روکش نمودن دندان می توان بر این نقیصه، چیره شد.
چه عواملی در موفقیت معالجه ریشه دندان نقش دارند؟
مهارت دندانپزشک ، تعداد ریشه ها قطر و انحنای آنها، وجود ریشه ها و کانالهای اضافی و جانبی، نوع و قدرت بیماری زایی میکروبها، دفاع بدن و نوع بیماری پالپ در پیش آگهی درمان مؤثرند.
مهارت دندانپزشک ، تعداد ریشه ها قطر و انحنای آنها، وجود ریشه ها و کانالهای اضافی و جانبی، نوع و قدرت بیماری زایی میکروبها، دفاع بدن و نوع بیماری پالپ در پیش آگهی درمان مؤثرند.
آیا دندانی که معالجه ریشه دندان شده و هنوز درد دارد را باید کشید؟
معمولاً به دنبال معالجه ریشه دندان، از چند ساعت تا چند روز به درجاتی ممکن است دندان، درد داشته باشد که با تجویز داروهای مسکن برطرف میگردد و جای نگرانی ندارد.
معمولاً به دنبال معالجه ریشه دندان، از چند ساعت تا چند روز به درجاتی ممکن است دندان، درد داشته باشد که با تجویز داروهای مسکن برطرف میگردد و جای نگرانی ندارد.
اگر درمان ریشه دندان شکست خورد، درمان بعدی چیست؟
اکثر دندانهایی که معالجه ریشه آنها با عدم موفقیت همراه شده را می توان با جراحی های اندودونتیکس نجات داد. دندانپزشک بعد از بیحس نمودن، لثه دندان را به آرامی کنار زده و اقدام به قطع انتهای ریشه نموده و آن را از انتها نیز ترمیم می: ند و دوباره لثه را می دوزد. آیا فقط ممکن است پوسیدگی بسیار وسیع بوده و قسمت اعظم آن نیز از بین رفته باشد و درد نداشته باشد و یا در اثر ضربه حتی در سالهای دور، پالپ آن مرده، ولی دردی نداشته باشد. عدم وجود درد دال بر نفی بیماری پالپ و یا عدم نیاز به درمان نمی باشد.
اکثر دندانهایی که معالجه ریشه آنها با عدم موفقیت همراه شده را می توان با جراحی های اندودونتیکس نجات داد. دندانپزشک بعد از بیحس نمودن، لثه دندان را به آرامی کنار زده و اقدام به قطع انتهای ریشه نموده و آن را از انتها نیز ترمیم می: ند و دوباره لثه را می دوزد. آیا فقط ممکن است پوسیدگی بسیار وسیع بوده و قسمت اعظم آن نیز از بین رفته باشد و درد نداشته باشد و یا در اثر ضربه حتی در سالهای دور، پالپ آن مرده، ولی دردی نداشته باشد. عدم وجود درد دال بر نفی بیماری پالپ و یا عدم نیاز به درمان نمی باشد.
ROOT CANAL TREATMENT
 | Root canal is a treatment to repair and save a badly damaged or infected tooth instead of removing it. The term "root canal" comes from cleaning of the canals inside a tooth's root. Decades ago, root canal treatments often were painful. With dental advances and local anesthetics, most people have little if any pain with a root canal. In fact, it's probably more painful living with a decayed tooth. Root canal alternatives include extracting the damaged tooth and replacing it with a dental implant, bridge or removable partial denture. Those options are often more complex and costly than having a root canal. |
 | Teeth have a soft core called dental pulp. The pulp extends from the crown — the visible part of the tooth — to the tip of the tooth's root in the jawbone. The pulp contains nerves, blood vessels and connective tissue. When a tooth is cracked or has a deep cavity, bacteria can enter the pulp. Left untreated, bacteria and decaying material can cause a serious infection or a tooth abscess, leading to pulp death, bone loss and loss of the tooth itself. Signs and symptoms may include swelling around your face and neck, a hole in your tooth, toothache or tooth pain, gum swelling, and temperature sensitivity. |
 | A root canal is usually done by an endodontist or a general dentist. The root canal usually takes one to three visits. First, you have dental X-rays to check the extent of damage. You also receive a local anesthetic to control pain. A rubber-like sheet called a dental dam is put in your mouth to keep the tooth clean, protected and free of saliva. Decay is removed, and an opening is made through the crown of the tooth to gain access to the pulp chamber. Using small dental instruments, the infected or diseased pulp is removed. |
 | After the diseased pulp is removed, the pulp chamber and root canals are flushed and cleaned. The root canals may be reshaped and enlarged to allow better access for filling later. Before permanently filling the root canals, they should be clean of all infection and dried. Medication is sometimes put into the pulp chamber and root canal to clear any infection. The tooth may be left open to drain for several days. If infection has spread beyond the tooth, you may need a prescription for antibiotics. If the root canal requires multiple visits, a temporary filling is placed in the crown to protect the tooth and keep out debris and saliva. Avoid biting or chewing on the tooth until it's been treated and restored. |
 | After cleaning and drying, it's time to fill the interior of the tooth — the empty pulp chamber and root canals. You may not need additional anesthetic for this step. If you had a temporary filling placed, that will be removed to allow access to the inside of the tooth. A sealer paste and rubber compound is used to fill the tooth, followed by an adhesive filling to make sure the root canals are protected from saliva. |
 | The final stage of the root canal is restoring your tooth. Because the tooth typically has a large filling or is weakened from extensive decay, it needs to be protected from future damage and returned to normal function. This is usually done by placing a crown — a realistic-looking artificial tooth. A crown is made of gold, porcelain or porcelain fused to metal. It can be tinted to match the exact color of your other teeth. Sometimes, a metal rod must first be inserted in the tooth for structural support and to keep the crown in place. Ask your dentist or endodontist about other restoration options. |
 | After your root canal, your restored tooth with the new crown should work normally and look cosmetically pleasing. If you follow good dental and oral hygiene, your restored tooth could last a lifetime. The first few days after your root canal, the tooth may be sensitive. Over-the-counter pain medications can help. If pain or pressure lasts more than a few days, be sure to talk to your dentist. |
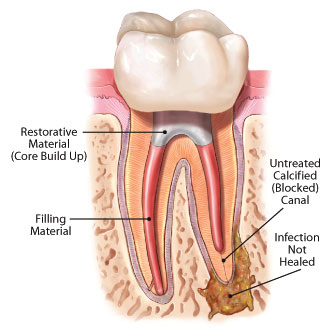
Root Canal Retreatment
| Retreatment is necessary when bacteria have re-entered the tooth. This is usually due to decay or untreated canal areas. The patient may experience swelling or pain in chewing. Sometimes a patient may have no symptoms, but an x-ray shows that there is a problem with a tooth that has previously undergone root canal therapy. |  |
What Happens During Root Canal Retreatment?
 | Step one:After the tooth is "numbed", the canal system will be reopened to remove the previous root canal material. This may involve removing a crown, post and core material. Sometimes we are able to make a small hole in the existing restoration and work through that opening. The canals are then thoroughly cleansed and shaped. |
Step two:The canals are refilled with gutta-percha and the opening is sealed with a sterile cotton pellet and a temporary filling. |  |
 | Step three:The tooth is usually restored within a couple of weeks. If your existing crown can be saved, then you will need to have it repaired. If you do not have a crown, it will probably be recommended. With time, the bone will heal where the bacteria was removed. |
Root Canals | ||
|
| The following represents a typical endodontic case. Each phase of the treatment provides a general narrative along with both digital radiographs and images, as well as dental illustrations to assist in the case presentation. | |||
| Phase 1. Evaluation. This stage of endodontic treatment typically begins with a referral from your general dentist requesting the endodontist evaluate a particular tooth or area. Indicators can often be tooth sensitivity or soreness, information detailed on the endodontic FAQ page. The endodontist will utilize an array of tests to determine the problem area or areas and then inform the patient of their findings. | |||
 |  | ||
| Phase 2. Initiation of Treatment. Following the evaluation, the patient generally decides on the best course of treatment for the tooth in question. At this stage, if treatment is required and requested, the endodontist will 'open' up the problem tooth, remove the infected pulp, and place a medicated packing into the pulp chamber. This medication usually remains in place for 10 to 14 days, helping to ensure that the infecting bacteria is eliminated. The tooth opening will then be closed using a temporary material and a follow-up appointment will be set. | |||
 |  | ||
| Phase 3. Completion of Treatment. At the follow-up appointment, the endodontist will inspect the treated tooth to appraise the progress of the medication in eliminating the infection. If successful, the tooth will be re-opened, the medicated removed, and the root canal treatment initiated. The endodontist will begin to obturate the root canals themselves, cleaning and smoothing them with special files. Once confident that all debris has been removed and the canals are sufficiently prepared, the endodontist will fill the open canals with permanent filling materials. Finally, the endodontist will close off the root canals from infection with another placement of temporary sealant. In some cases, depending on the endodontist's evaluation of the tooth, a permanent restoration might be placed instead of a temporary one. | |||
 |  | ||
 |  | ||
 |  | ||
| Phase 4. Follow-Up. Critical to the success of the endodontic treatment, a patient will be directed to return to their general dentist for the placement of a permanent crown. It cannot be stressed enough how important this phase of the treatment is. The temporary seal used by the endodontist to 'close' of the areas of the root canal has a general lifespan of 4 weeks, or less. Following that time frame, it is certain that the temporary bond will be compromised and bacteria will begin to re-infect the treated area. Therefore, a patient who receives endodontics MUST complete the process by having a crown placed over the treated tooth by their respective general dentist. Failure to complete the process with a crown will ensure the reinfection of the endodontically treated tooth, often leading to a complete root canal retreatment or dental extraction. | |||
 |  | ||
Root Canal Treatment
Anatomy & Physiology
Root canal treatment involves treatment of the pulp space within a tooth. The dental pulp is a soft tissue, which is within a tooth under the enamel and dentine. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue and creates the hard tissues of the tooth during development. The dental pulp occupies both the crown and root of the tooth and enters through an opening in the end of the root.
Root canal treatment involves treatment of the pulp space within a tooth. The dental pulp is a soft tissue, which is within a tooth under the enamel and dentine. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue and creates the hard tissues of the tooth during development. The dental pulp occupies both the crown and root of the tooth and enters through an opening in the end of the root.
Indications
Root canal treatment becomes necessary when the inside of the tooth becomes infected or inflamed. This usually happens as a result of deep decay, trauma to the tooth and repeated operative procedures. Any of these may result in signs of pulp damage such as prolonged sensitivity to temperature, swelling or a change in tooth colour. Frequently pulp death can occur with no symptoms.
Root canal treatment becomes necessary when the inside of the tooth becomes infected or inflamed. This usually happens as a result of deep decay, trauma to the tooth and repeated operative procedures. Any of these may result in signs of pulp damage such as prolonged sensitivity to temperature, swelling or a change in tooth colour. Frequently pulp death can occur with no symptoms.
Anaesthetic
Treatment is usually performed under local anaesthesia.
Treatment is usually performed under local anaesthesia.
Technique
- Initially a thorough assessment is performed, which includes an examination of your mouth, the tooth in question and radiographs.
- A sheet of rubber is placed over the tooth after the administration of the local anaesthetic. This helps keep bacteria from saliva away from the tooth and contains irrigating solutions that are used to disinfect the root canal.
- An access opening is made through the crown of the tooth into the pulp cavity. This facilitates the placement of root canal instruments into the pulp space. Further radiographs are required to help determine the length of the tooth root (Fig. 1).
- The root canals are shaped by instruments and cleaned with disinfectant irrigating solutions. Once this is completed the root canals are filled usually with gutta-percha and a sealing cement. Radiographs are then taken to establish the filling is satisfactory (Fig. 2). A filling is then placed to seal the access opening; this may be temporary or definitive.
- It is essential the tooth is restored definitively after the root canal treatment, as this serves to support the tooth and help reduce the chance of re-entry of bacteria. Follow-up radiographs are recommended to ensure the infection has responded to treatment.
 |
| Figure 1. Root canal instrument placement. |
 |
| Figure 2. Radiograph showing filled root canals. |
Length of Operation
The length of the procedure varies. Straightforward cases may be completed in ½ to 1 hour. More demanding teeth may take considerably longer - sometimes over two hours. Such cases (and very infected teeth) will frequently necessitate more than one visit before the procedure is completed.
The length of the procedure varies. Straightforward cases may be completed in ½ to 1 hour. More demanding teeth may take considerably longer - sometimes over two hours. Such cases (and very infected teeth) will frequently necessitate more than one visit before the procedure is completed.
Time in Hospital
All dentists receive training in root canal treatment at Dental School and most management is performed in General Dental Practice.
All dentists receive training in root canal treatment at Dental School and most management is performed in General Dental Practice.
Time Off Work
This will depend on the complexity of the case. It is normal to have some slight discomfort for 2 or 3 days after treatment. This, however, can usually be controlled with over-the-counter analgesics.
This will depend on the complexity of the case. It is normal to have some slight discomfort for 2 or 3 days after treatment. This, however, can usually be controlled with over-the-counter analgesics.
Outcome/Prognosis
Root canal therapy is not 100% successful. Straightforward cases may be expected to work 95% of the time; more complex teeth, however, have a lower prognosis of 65-85%. This success cannot be guaranteed. The lower success rates are usually associated with very infected teeth or teeth which have failed to respond to initial treatment or have become re-infected.
Root canal therapy is not 100% successful. Straightforward cases may be expected to work 95% of the time; more complex teeth, however, have a lower prognosis of 65-85%. This success cannot be guaranteed. The lower success rates are usually associated with very infected teeth or teeth which have failed to respond to initial treatment or have become re-infected.
Alternative Treatments
The only alternative treatment that will remove the infection is extraction of the tooth.
The only alternative treatment that will remove the infection is extraction of the tooth.
Links:
http://www.eastcountyrootcanal.com/case_of_the_month
http://www.eastcountyrootcanal.com/patient_info

هیچ نظری موجود نیست:
ارسال یک نظر
توجه:فقط اعضای این وبلاگ میتوانند نظر خود را ارسال کنند.